Hi, my name is Tengfei Xu. I am a vibrant young researcher with a profound interest in AI4science. During my undergraduate studies at Dalian university of technology, I participated in the esteemed Qian Lingxi Excellence in Education Program and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Engineering Mechanics. Following my excellent academic performance, I was recommended for exemption from the entrance examination and am currently pursuing a Master’s degree in Computational Mechanics at the same university, with an expected graduation date of June 2025. I am actively seeking full-time internship opportunities and a doctoral position in AI4science to further explore the intersection of artificial intelligence and various scientific disciplines.
Publications
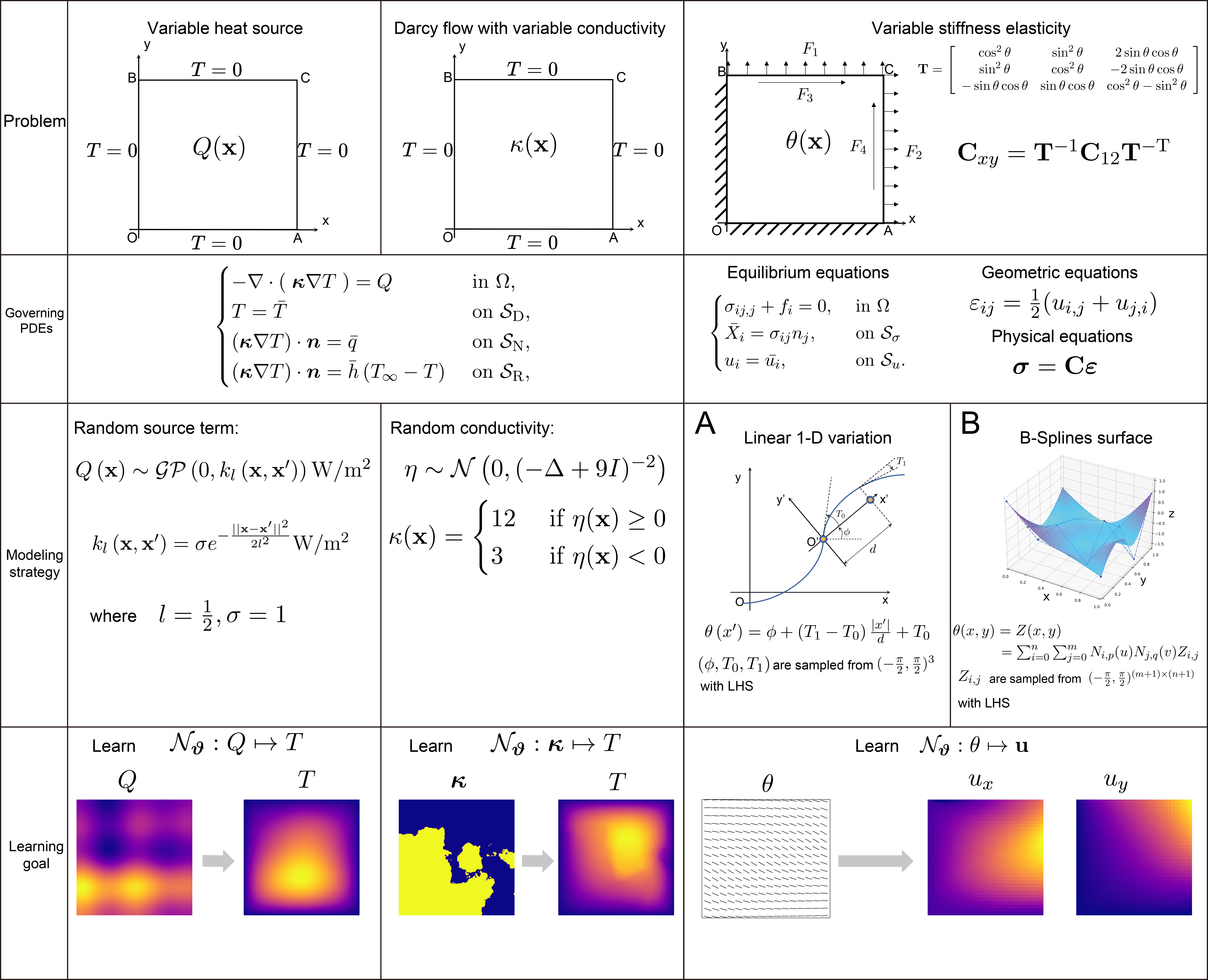
Variational operator learning: A unified paradigm marrying training neural operators and solving partial differential equations
Tengfei Xu, Dachuan Liu, Peng Hao, Bo Wang
- Neural operators as novel neural architectures for fast approximating solution operators of partial differential equations (PDEs), have shown considerable promise for future scientific computing. However, the mainstream of training neural operators is still data-driven, which needs an expensive ground-truth dataset from various sources (e.g., solving PDEs’ samples with the conventional solvers, real-world experiments) in addition to training stage costs. From a computational perspective, marrying operator learning and specific domain knowledge to solve PDEs is an essential step for data-efficient and low-carbon learning. We propose a novel data-efficient paradigm that provides a unified framework of training neural operators and solving PDEs with the domain knowledge related to the variational form, which we refer to as the variational operator learning (VOL). We develop Ritz and Galerkin approach respectively with finite element discretization for VOL to achieve matrix-free approximation of the energy functional of physical systems and calculation of residual tensors derived from associated linear systems with linear time complexity and O(1) space complexity. We then propose direct minimization and iterative update as two possible optimization strategies. Various types of experiments based on reasonable benchmarks about variable heat source, Darcy flow, and variable stiffness elasticity are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of VOL. With a label-free training set, VOL learns solution operators with its test errors decreasing in a power law with respect to the amount of unlabeled data. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first study that integrates the perspectives of the weak form and efficient iterative methods for solving sparse linear systems into the end-to-end operator learning task.
My contribution in this work:
Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal Analysis, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization.
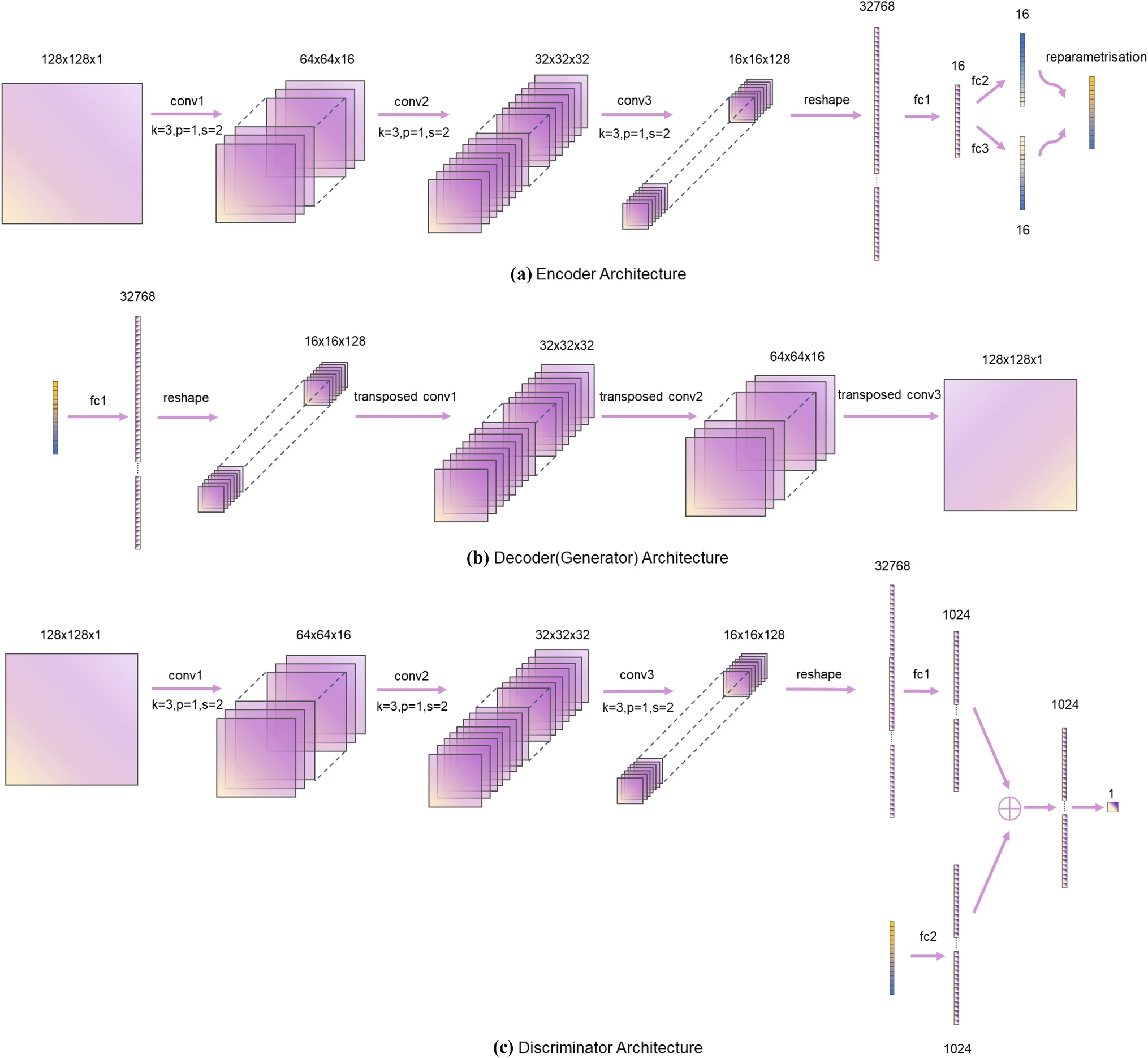
Intelligent optimization of stiffener unit cell via variational autoencoder-based feature extraction
Dachuan Liu, Peng Hao, Tengfei Xu, Yingjie Zhu, Xuanxiu Liu, Bo Wang, Gang Li
- Grid-stiffened structures are widely used in industrial equipment, where the layout of stiffener unit cells is critical in the structural performance. However, owing to the lack of design techniques, existing stiffener unit cell designs are often achieved only by comparative selection among several common cell configurations. In this study, a deep learning-based intelligent optimization framework for the stiffener unit cell of grid-stiffened panels was proposed. First, a database containing nearly 10,000 stiffener unit cells was generated by traversal while considering the manufacturability. Feature extraction was then performed on the generated database using a variational autoencoder and mapped to a 16-dimensional continuous latent design space according to geometric features. Subsequently, in this latent space, a Gaussian process model was established, and the maximum expected improvement criterion was utilized to drive the model update and optimization search, thus realizing data-driven optimization for the stiffener unit cell of grid-stiffened panels. In three typical numerical examples, compared with the best of the traditional stiffener unit cells, the obtained optimal designs were improved by 25.61%, 25.88%, and 10.66%, respectively, demonstrating the effectiveness of this method as an alternative stiffener unit cell design method. Furthermore, this study also indicates the significant potential of geometric feature extraction and further structural layout optimization via deep learning.
My contribution in this work:
Software, Validation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing, Review & Editing, Visualization.
Specifically, in this study, I implemented an enhanced variational autoencoder model, incorporating elements of a generative adversarial network (VAE-GAN), as originally proposed by Anders Boesen Lindbo Larsen, et al. Related code and datasets link. And I wrote the technique details and drew figures related VAE-GAN in the manuscript.
My Blog
I share my debugging and technical notes here since 2018. As of March 19, 2024, the total views of the blog have exceeded 500k, with over 250 likes and 580 collections.
My Channel
I share my academic talks here since 2022. As of March 19, 2024, the total views of the channel have exceeded 40k, with over 400 likes and 350 friends.
I will keep updating more interesting contents in math, physics and engineering in this channel when I’m free.